The ending of the story is the most important part of the story, along with the climax. The ending of the story determines the fates of all the characters in it, and any further implications for a sequel. If the story has a bad ending, it may ruin the mood of the entire story and possibly infuriate the reader. The ending plays a key role in how our brains react to the story.
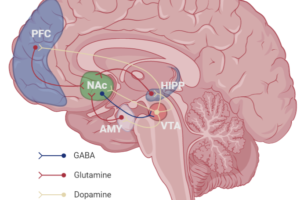
Our brains release immense amounts of dopamine throughout a story, but the ending allows for our brains to process it. The falling action sets up the destinies of the characters and the actions that they take that lead them ultimately to the end. There are four main types of endings, and each stimulates our brains in a different way.
The first and the most common ending is the happy ending. This kind of ending causes the Limbic System of our brains to release dopamine and gives us a “feel-good” feeling. These kinds of endings are common in children’s stories (the good guy defeats the bad guy and lives happily ever after). However, they are also very predictable. After watching or reading enough stories, our brains tend to expect a happy ending, and this leads to a reduced release of dopamine at the end of a story. At times, it could even lead to annoyance from the readers at a normal ending.
The second ending is the cliffhanger. This kind of ending causes our brains to trigger the release of adrenaline, which makes us feel anxious and on the edge of our seat. It leaves us wanting more and we often resent such endings as sequels to those stories, if they exist at all, often take time to make and often lead to fans making their own version of an ending. This ending is usually only utilized in adult novels and not in children’s books.
In conclusion, these two endings are very common in stories and various chemicals are released in the readers’ brains, depending on which type of ending is shown in a story.
Source: The Science of the Story: https://news.berkeley.edu/berkeley_blog/the-science-of-the-story/





Most Commented Posts